What Is GFCI & How Does It Work?
Electricity powers almost everything in our homes, but it comes with risks especially in places where water is nearby. A quick splash, a damp hand, or a leaking pipe can turn an everyday outlet into a serious shock hazard. That’s why modern homes rely on GFCI outlets and GFCI breakers. These devices are designed to cut power instantly when something goes wrong, protecting you and your family from potentially life-threatening shocks.
If you’ve ever noticed an outlet with TEST and RESET buttons in your bathroom, kitchen, or garage, you’ve already seen a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) in action. But what is GFCI exactly, and how does it work? Let’s dive in.
What Is GFCI and Why GFCI Exists?

A Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) is a safety device that shuts power off the moment it senses electricity leaking somewhere it shouldn’t—like through water or a person. It trips in fractions of a second to prevent shock.
A ground fault happens when electricity takes an unintended path to the ground. Instead of flowing safely through wires, current leaks through water, a metal surface, or even a person.
For example:
- Using a hair dryer with wet hands in the bathroom
- Running an extension cord outdoors on damp grass
- A frayed wire under the sink touching a wet pipe
In all these cases, the risk of electrical shock is real. Before GFCI protection became standard, these accidents often resulted in injuries or even fatalities. Today, GFCIs are one of the most important tools for home electrical safety.
How Does a GFCI Work?
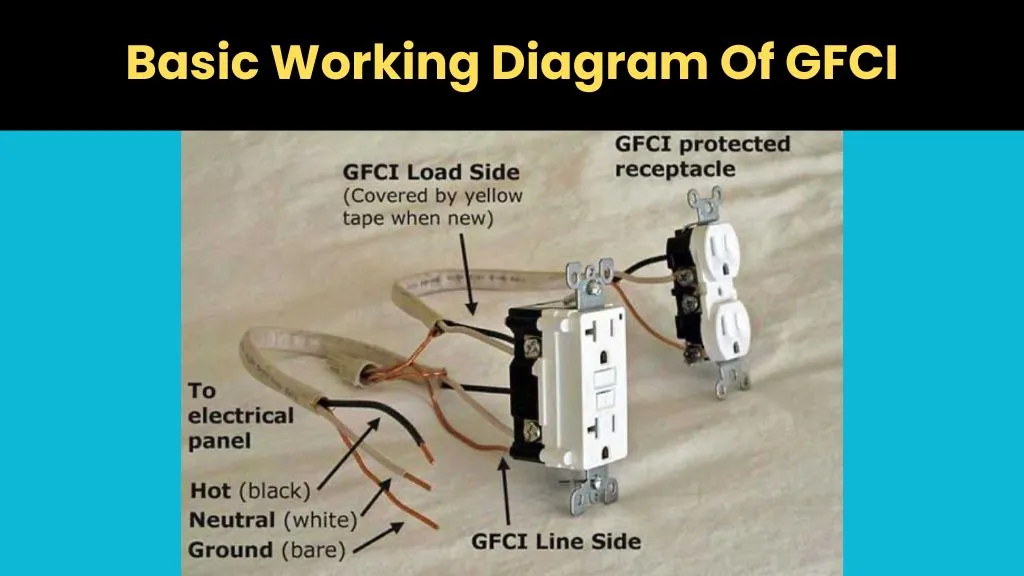
The diagram above shows the working of a GFCI outlet. Power from the electrical panel flows into the line side (black for hot, white for neutral, bare for ground). From there, the GFCI monitors the current going in and out. If it detects even a small imbalance—such as current leaking to the ground through water or a person—it immediately trips, cutting power.
The load side, which is covered by yellow tape when new, allows the GFCI to extend protection to additional outlets downstream. In this setup, the GFCI not only safeguards the main receptacle but also protects the connected outlet shown in the image. Think of it as a leak detector for electricity: the moment power escapes its intended path, the GFCI cuts it off in about 1/40 of a second to prevent shocks.
Types of GFCI Devices
There isn’t just one type of GFCI. Depending on your home setup, you may encounter different versions:
1. GFCI Outlet (Receptacle)
This is the most common type. It looks like a regular wall outlet but with TEST and RESET buttons. A GFCI outlet can protect not only itself but also other outlets downstream on the same circuit.
2. GFCI Circuit Breaker
Installed directly in your electrical panel, a GFCI breaker protects an entire circuit. This means every outlet and device connected to that circuit benefits from GFCI protection. It’s especially useful for large areas like kitchens or basements.
3. Portable GFCI
These plug-in devices are perfect for temporary use. For example, if you’re using power tools outdoors, a portable GFCI ensures safety even if the outlet isn’t already protected. They’re also common on extension cords designed for outdoor work.
Where Do You Need GFCI Outlets?
Because water and electricity don’t mix, GFCIs are required or recommended in many areas of a home:
- Bathroom GFCI outlet – Protects against shocks when using hair dryers, shavers, or curling irons.
- Kitchen GFCI outlet – Essential for areas near sinks, dishwashers, and garbage disposals.
- Outdoor GFCI outlet – Must for patios, gardens, and power tools used outside.
- Garage and basement GFCI outlet – Prevents shock risks in damp or unfinished spaces.
- Laundry room – Protects washers and utility sinks from electrical hazards.
Safety Benefits of GFCI Protection
Here’s what makes GFCI outlets and breakers so important:
- Shock protection: Stops dangerous currents in milliseconds.
- Preventing electrical fires: Reduces risks caused by leaking or faulty wiring.
- Works even without ground: A GFCI can still protect you in older homes with ungrounded outlets.
- Peace of mind: Knowing your outlets have GFCI protection lets you and your family use appliances safely around water.
How to Recognize and Use a GFCI Outlet
Spotting a GFCI outlet is simple just look for the familiar TEST and RESET buttons on the face of the receptacle. These outlets are designed for both protection and convenience. To ensure yours is working properly, test it at least once a month by pressing the TEST button. The outlet should immediately cut power to anything plugged in. Then press RESET to restore power. If the outlet trips during regular use, pressing RESET will restore function. However, if your GFCI trips frequently, that’s a sign to check for underlying issues such as water leaks, damaged cords, or faulty appliances.
Common Misconceptions About GFCI
One common myth is that they replace circuit breakers. This isn’t true circuit breakers protect your home’s wiring from overloads, while GFCIs are designed specifically to protect people from electric shock. Another misconception is that GFCIs last forever. In reality, they can wear out, and most need replacing every 10–15 years or sooner if they stop functioning properly. Finally, some believe GFCIs prevent all shocks. While they don’t protect against every type of electrical contact such as line-to-line shocks. They do drastically reduce the risk of dangerous ground faults, which are the most common cause of electrocution.
Best Practices for Homeowners
- Always install GFCI outlets in wet-prone areas.
- Test outlets monthly to ensure they work.
- Replace outlets that don’t reset or test correctly.
- Consider upgrading to GFCI breakers for whole-circuit protection.
- For temporary outdoor work, use a portable GFCI for added safety.
Further Reading:
Do Garbage Disposals Need GFCI?
Do Garbage Disposals Have Blades? The Truth Behind Kitchen Myths
How to Recycle an Old Garbage Disposal
Are Garbage Disposals Required By Code in USA?
Conclusion
At its core, a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) is a small but powerful device that instantly shuts off power when it detects even the slightest electrical leak. This rapid response prevents dangerous shocks and makes GFCIs essential in areas where water and electricity often meet—such as kitchens, bathrooms, garages, basements, and outdoor spaces. Their role in modern home safety is simple yet critical: they add an extra layer of protection that standard outlets alone cannot provide.
The real value of GFCIs lies in their simplicity and effectiveness. They’re affordable, easy to install, and provide peace of mind by reducing everyday electrical risks. Regular testing, timely replacement, and considering upgrades like GFCI breakers for whole-circuit coverage can make homes even safer. In the end, embracing GFCI protection is not just about following good practice—it’s about taking proactive steps to safeguard your family and make your living space truly secure.
The Author

Muhammad Nabeel Dar has worked in the waste management industry for over 10 years, specializing in residential waste systems and kitchen efficiency solutions. He writes about practical home improvements, cost-effective appliance choices, and sustainable waste management practices that help homeowners make informed decisions. His hands-on experience with both commercial and residential waste systems provides unique insights into what actually works well in real-world home environments versus what just sounds good in marketing materials.







